Sound and Ultrasound
Loudness and amplitude
Sounds are produced when objects vibrate.
The sound travels as longitudinal waves.
These waves can be converted into electrical signals which can be displayed on an oscilloscope.
The height of a wave, from a midline to the top of a crest or bottom of a trough, is called the amplitude.
The louder a sound is, the bigger the vibrations are, and the bigger the amplitude of the wave produced.
A soft, or quiet, sound has a smaller amplitude.

Pitch and frequency
The number of vibrations per second is called the frequency.
Frequency is measured in units called hertz (Hz).
The pitch of a sound is determined by its frequency.
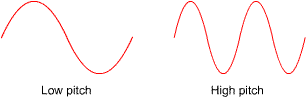
A high pitched sound has a high frequency, and therefore a short wavelength.
A low pitch sound has a low frequency and therefore a long wavelength.
The two waves shown below would be of different pitch, but would be the same volume because the amplitude is the same.
Ultrasonic waves
The range of sound frequencies that humans can hear is between 20 and 20,000 Hz.
Electronic systems can produce electrical oscillations with any frequency.
These electrical oscillations can be used to produce ultrasonic waves (ultrasound).
These have a frequency above 20.000 Hz, so are too high to be detected by the human ear.
Ultrasonic waves are used in industry for cleaning delicate mechanisms without the need to take them apart.
The object to be cleaned is placed in a tank of liquid through which the waves travel, to dislodge the dirt.
They are also used for quality control in the manufacture of sheet metals.
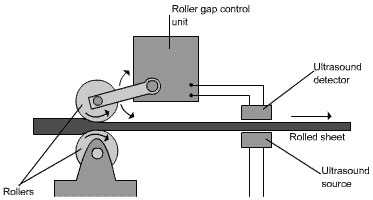
The diagram shows how ultrasound can be used to monitor the thickness of the sheet.
If the sheet is too thin, the detector will detect a higher amplitude of ultrasonic waves and send a signal to the control unit to increase the gap between the rollers.
If the sheet is too thick, the amplitude will be smaller and the detector will send a signal to the control unit to decrease the gap between the rollers.
Ultrasonic waves are partly reflected when the meet the boundary between two different substances.
The time taken for the reflections to reach a detector, which is usually placed near to the source, is used to calculate how far away the boundary is. The further away it is, the longer it takes for the reflection to be detected.
This idea is used in medicine to check the development of a baby in the womb (pre-natal scanning). This is much safer than using X-rays, because X-rays damage body cells.
In industry the same principle is used to detect flaws in metal castings.
The reflected signals are processed by a computer to produce a visual display.
Document Actions

 Like us on Facebook
Like us on Facebook