Reactions Involving Enzymes
Properties of Enzymes
Living cells use chemical reactions to produce new materials.
These chemical reactions are controlled by special chemicals called enzymes .
Enzymes are biological catalysts. They speed up chemical reactions in living cells.
All enzymes are protein molecules.
Each one catalyses a specific reaction.
Each one works best at a particular pH and temperature.
They work faster at higher temperatures, up to about 45ºC. Above this they become denatured (damaged).
We use enzymes in industry and at home to bring about reactions at normal temperatures and pressures that would otherwise require expensive energy demanding equipment.
Yeast and Bacteria
Yeast cells convert sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide during anaerobic respiration.
The process is also called fermentation.
sugar ![]() alcohol + carbon dioxide
alcohol + carbon dioxide
We use this reaction to produce the alcohol (ethanol) in beer and wine.
We use Yeast in bread making to produce bubbles of carbon dioxide which get trapped in the dough and make it rise.
Bread doesn’t taste of alcohol because it gets evaporated off during baking.
The test for carbon dioxide is to bubble the gas through limewater .
It turns from clear to cloudy (milky).
Bacteria are used to make yoghurt.
The bacteria convert the sugar in milk (lactose) into lactic acid, which gives yoghurt its sour taste.
Uses of Enzymes
Biological detergents may contain protease (protein –digesting) and lipase (fat-digesting) enzymes which break down stains, like blood and food, which are otherwise difficult to remove.
They digest them into soluble molecules which dissolve in the water.
Biological detergents work best below 45ºC. Above this the enzymes become denatured.
Proteases are used to pre-digest the protein in baby foods to make them easier for babies to digest.
Carbohydrases are used to convert starch syrup into glucose syrup.
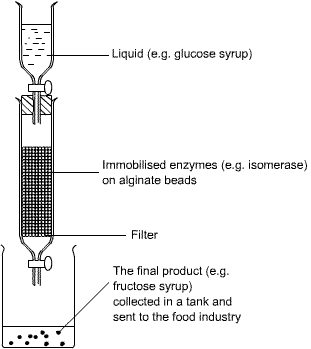
Isomerase is used to convert glucose syrup into fructose syrup. Fructose tastes much sweeter. This means less can be used in slimming foods.
Industrial issues
Where organisms are used in industrial processes they are usually stabilised and kept in controlled conditions to ensure that they keep functioning for long periods of time.
Enzymes are usually immobilised (held in place) by trapping them in an inert solid support or carrier such as alginate beads.
The reactants can be passed over them and the products removed without losing the enzyme.
A continuous production process is usually used, rather than a batch process.
This means the product is made continually and is easily separated from the enzymes and reactants.
Production does not have to be stopped to remove the products, the products are pure and there is less wastage.
Document Actions

 Like us on Facebook
Like us on Facebook