Gynaecologist/Obstetrician
Tasks & duties
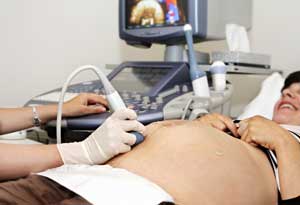
Gynaecologists/obstetricians may do some or all of the following:
-
identify and treat problems of the female reproductive system such as infertility and bladder problems
-
advise on the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases
-
consult and treat patients with abnormal cervical smears and heavy menstrual bleeding
-
check for and treat ovarian cysts and check for cancer of the female reproductive tract
-
perform surgery when necessary
-
examine and care for pregnant women
-
deliver babies
-
check the progress of mothers
-
advise on family planning
-
write notes to keep a record of their patients' progress
-
consult with colleagues about treatment for patients
Specialisations
Gynaecologists/obstetricians may move into sub-specialties such as:
-
cancer surgery
-
ultrasound scanning
-
high-risk pregnancies
-
urogynaecology (the diagnosis and treatment of incontinence in women)
-
fertility
Skills & knowledge
Gynaecologists/obstetricians need to have:
-
knowledge of anatomy and how the human body works, with in-depth knowledge about pregnancy and the female reproductive system
-
knowledge of different diseases and illnesses
-
up-to-date knowledge of new research, treatments and medical practices
-
medical and surgical skills
-
diagnostic, analytical and interpreting skills
-
communication skills
-
an awareness and understanding of other cultures and their attitudes to medical treatment
-
knowledge of medical ethics and the law
-
decision-making and problem-solving skills
-
organisational and time management skills
-
report writing skills
Entry requirements
To become a gynaecologist/obstetrician you need to have a Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBChB). You must then spend two years as a house surgeon and another six years in specialist training.
The University of Auckland and the University of Otago are the only two providers of the MBChB degree in New Zealand.
Secondary education
A tertiary entrance qualification is required to enter further training, but a Scholarship, an A Bursary or NCEA equivalent is preferred. Useful subjects include maths, chemistry, physics, biology and English.
Tertiary education
To enter the MBChB you need to complete the first year of a Bachelor of Health Science or a Bachelor of Science (Biomedical). Your first-year final grade is also determined by non-academic achievements including the Undergraduate Medicine and Health (UMAT) admission test and/or interview.
Alternatively, you can complete a related health sciences degree and apply for graduate entry to the MBChB programme. Graduate applicants must also take the UMAT admission test.
Training on the job
Gynaecologists/obstetricians are required to earn at least 150 points every three years by doing continuing professional development to keep up to date with developments in their field.
Professional development is approved and audited by the Royal Australian & New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists and may include teaching, reading approved medical journals, research, and attending medical lectures and conferences.
Registration
Gynaecologists/obstetricians must have fellowship of the Royal Australian & New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists and be registered with the Medical Council of NZ.
Related courses
Medical Science
Obstetrics and Gynaecology
For more information, please refer to Career Services.
Document Actions
