Hospital Nurse
Tasks & duties
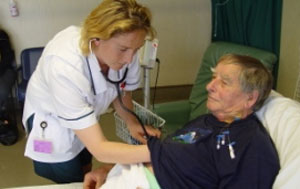
Hospital nurses may do some or all of the following depending on their area of specialisation:
-
take a comprehensive nursing history (to find out how the patient has been nursed in the past) and plan appropriate care to meet identified needs
-
discuss, plan and carry out nursing care to improve patients' health
-
monitor the condition of patients and record important changes
-
provide nursing treatment and therapy, and patient-centred care
-
give and monitor medications and intravenous drugs
-
educate patients and their families about health needs
-
check equipment and supplies
-
arrange discharge planning
-
arrange for patients to have treatment and/or care after they have been discharged from hospital
-
direct and delegate to second-level nurses and caregivers
-
work with other health professionals to meet the needs of patients' caregivers, whānau and supporters
Specialisations
Nursing is a broad discipline and most nurses employed in a hospital will develop skills in a specialist area of nursing practice. This may include areas such as:
-
mental health
-
midwifery
-
child health
-
aged care
-
cancer nursing
-
intensive care
-
operating theatre
-
community health
-
workplace health and safety
Skills & knowledge
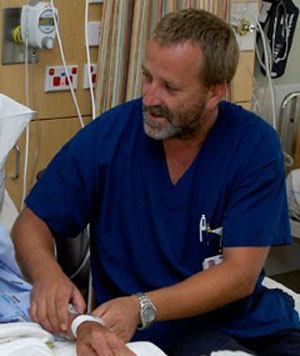
Hospital nurses need to have:
-
excellent nursing skills and knowledge of different nursing methods
-
knowledge of how the human body works
-
knowledge of different diseases and illnesses
-
knowledge of medicines and treatments, and the effect these have on patients
-
an ability to observe, monitor and assess patients' conditions
-
knowledge of how to use a variety of technical equipment, such as ventilation machines
-
an understanding of nursing law and legislation
-
communication and people skills, including good listening skills
-
excellent time management skills
-
decision-making skills
Entry requirements
To become a hospital nurse you need to have a Bachelor of Nursing degree. You also need to be registered with the Nursing Council of New Zealand, and have a current Annual Practising Certificate.
Secondary education
At least four years of secondary education is required to enter tertiary training, although five years is preferred. Useful subjects include English, maths, chemistry and biology.
Training on the job
Hospital departments usually provide training for nursing specialities. Most hospitals hold regular lectures and seminars on a range of topics, as nurses need to keep up to date with training procedures and equipment.
Nurses may also undertake postgraduate programmes, which are available through polytechnics and some universities.
Registration
All hospital nurses must be registered with the Nursing Council of New Zealand.
Useful experience
Any experience in the health industry, such as work in rest homes, nursing homes or with people with disabilities is useful, as is counselling experience.
Related courses
General Medicine
Hauora (Maori Health)
Nursing
For more information, please refer to Career Services.
Document Actions
