Arctic Ocean
Geography
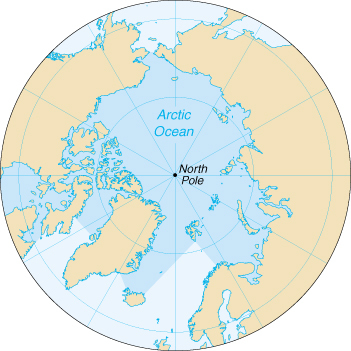
Location: | body of water between Europe, Asia, and North America, mostly north of the Arctic Circle |
Geographic coordinates: | 90 00 N, 0 00 E |
Map references: | Arctic Region |
Area: | total: 14.056 million sq km |
Area - comparative: | slightly less than 1.5 times the size of the US |
Coastline: | 45,389 km |
Climate: | polar climate characterized by persistent cold and relatively narrow annual temperature ranges; winters characterized by continuous darkness, cold and stable weather conditions, and clear skies; summers characterized by continuous daylight, damp and foggy weather, and weak cyclones with rain or snow |
Terrain: | central surface covered by a perennial drifting polar icepack that, on average, is about 3 meters thick, although pressure ridges may be three times that thickness; clockwise drift pattern in the Beaufort Gyral Stream, but nearly straight-line movement from the New Siberian Islands (Russia) to Denmark Strait (between Greenland and Iceland); the icepack is surrounded by open seas during the summer, but more than doubles in size during the winter and extends to the encircling landmasses; the ocean floor is about 50% continental shelf (highest percentage of any ocean) with the remainder a central basin interrupted by three submarine ridges (Alpha Cordillera, Nansen Cordillera, and Lomonosov Ridge) |
Elevation extremes: | lowest point: Fram Basin -4,665 m |
Natural resources: | sand and gravel aggregates, placer deposits, polymetallic nodules, oil and gas fields, fish, marine mammals (seals and whales) |
Natural hazards: | ice islands occasionally break away from northern Ellesmere Island; icebergs calved from glaciers in western Greenland and extreme northeastern Canada; permafrost in islands; virtually ice locked from October to June; ships subject to superstructure icing from October to May |
Environment - current issues: | endangered marine species include walruses and whales; fragile ecosystem slow to change and slow to recover from disruptions or damage; thinning polar icepack |
Geography - note: | major chokepoint is the southern Chukchi Sea (northern access to the Pacific Ocean via the Bering Strait); strategic location between North America and Russia; shortest marine link between the extremes of eastern and western Russia; floating research stations operated by the US and Russia; maximum snow cover in March or April about 20 to 50 centimeters over the frozen ocean; snow cover lasts about 10 months |
Economy | |
Economy - overview: | Economic activity is limited to the exploitation of natural resources, including petroleum, natural gas, fish, and seals. |
Transportation | |
Ports and harbours: | Churchill (Canada), Murmansk (Russia), Prudhoe Bay (US) |
Transportation - note: | sparse network of air, ocean, river, and land routes; the Northwest Passage (North America) and Northern Sea Route (Eurasia) are important seasonal waterways |
Document Actions

 Like us on Facebook
Like us on Facebook