Japan
Introduction | Japan |
Background: | In 1603, a Tokugawa shogunate (military dictatorship) ushered in a long period of isolation from foreign influence in order to secure its power. For 250 years this policy enabled Japan to enjoy stability and a flowering of its indigenous culture. Following the Treaty of Kanagawa with the US in 1854, Japan opened its ports and began to intensively modernize and industrialize. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Japan became a regional power that was able to defeat the forces of both China and Russia. It occupied Korea, Formosa (Taiwan), and southern Sakhalin Island. In 1931-32 Japan occupied Manchuria, and in 1937 it launched a full-scale invasion of China. Japan attacked US forces in 1941 - triggering America's entry into World War II - and soon occupied much of East and Southeast Asia. After its defeat in World War II, Japan recovered to become an economic power and a staunch ally of the US. While the emperor retains his throne as a symbol of national unity, actual power rests in networks of powerful politicians, bureaucrats, and business executives. The economy experienced a major slowdown starting in the 1990s following three decades of unprecedented growth, but Japan still remains a major economic power, both in Asia and globally. In 2005, Japan began a two-year term as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council. |
Geography | Japan |
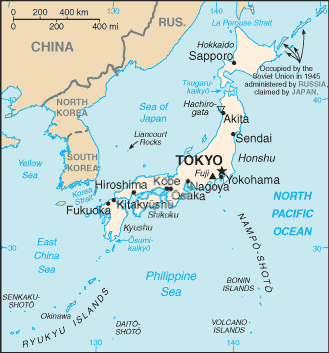
Location: | Eastern Asia, island chain between the North Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Japan, east of the Korean Peninsula |
Geographic coordinates: | 36 00 N, 138 00 E |
Area: | total: 377,835 sq km |
Land boundaries: | 0 km |
Coastline: | 29,751 km |
Maritime claims: | territorial sea: 12 nm; between 3 nm and 12 nm in the international straits - La Perouse or Soya, Tsugaru, Osumi, and Eastern and Western Channels of the Korea or Tsushima Strait |
Climate: | varies from tropical in south to cool temperate in north |
Terrain: | mostly rugged and mountainous |
Elevation extremes: | lowest point: Hachiro-gata -4 m |
Natural resources: | negligible mineral resources, fish |
Land use: | arable land: 11.64% |
Irrigated land: | 25,920 sq km (2003) |
Natural hazards: | many dormant and some active volcanoes; about 1,500 seismic occurrences (mostly tremors) every year; tsunamis; typhoons |
Environment - current issues: | air pollution from power plant emissions results in acid rain; acidification of lakes and reservoirs degrading water quality and threatening aquatic life; Japan is one of the largest consumers of fish and tropical timber, contributing to the depletion of these resources in Asia and elsewhere |
Environment - international agreements: | party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling |
Geography - note: | strategic location in northeast Asia |
People | Japan |
Population: | 127,463,611 (July 2006 est.) |
Age structure: | 0-14 years: 14.2% (male 9,309,524/female 8,849,476) |
Median age: | total: 42.9 years |
Population growth rate: | 0.02% (2006 est.) |
Birth rate: | 9.37 births/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
Death rate: | 9.16 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
Net migration rate: | 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
Sex ratio: | at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female |
Infant mortality rate: | total: 3.24 deaths/1,000 live births |
Life expectancy at birth: | total population: 81.25 years |
Total fertility rate: | 1.4 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
Nationality: | noun: Japanese (singular and plural) |
Ethnic groups: | Japanese 99%, others 1% (Korean 511,262, Chinese 244,241, Brazilian 182,232, Filipino 89,851, other 237,914) |
Religions: | observe both Shinto and Buddhist 84%, other 16% (including Christian 0.7%) |
Languages: | Japanese |
Literacy: | definition: age 15 and over can read and write |
Government | Japan |
Country name: | conventional long form: none |
Government type: | constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary government |
Capital: | Tokyo |
Administrative divisions: | 47 prefectures; Aichi, Akita, Aomori, Chiba, Ehime, Fukui, Fukuoka, Fukushima, Gifu, Gunma, Hiroshima, Hokkaido, Hyogo, Ibaraki, Ishikawa, Iwate, Kagawa, Kagoshima, Kanagawa, Kochi, Kumamoto, Kyoto, Mie, Miyagi, Miyazaki, Nagano, Nagasaki, Nara, Niigata, Oita, Okayama, Okinawa, Osaka, Saga, Saitama, Shiga, Shimane, Shizuoka, Tochigi, Tokushima, Tokyo, Tottori, Toyama, Wakayama, Yamagata, Yamaguchi, Yamanashi |
Dependent areas: |
|
Independence: | 660 B.C. (traditional founding by Emperor JIMMU) |
National holiday: | Birthday of Emperor AKIHITO, 23 December (1933) |
Constitution: | 3 May 1947 |
Legal system: | modeled after European civil law system with English-American influence; judicial review of legislative acts in the Supreme Court; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations |
Suffrage: | 20 years of age; universal |
Executive branch: | chief of state: Emperor AKIHITO (since 7 January 1989) |
Legislative branch: | bicameral Diet or Kokkai consists of the House of Councillors or Sangi-in (242 seats - members elected for six-year terms; half reelected every three years; 146 members in multi-seat constituencies and 96 by proportional representation) and the House of Representatives or Shugi-in (480 seats - members elected for four-year terms; 300 in single-seat constituencies; 180 members by proportional representation in 11 regional blocs) |
Judicial branch: | Supreme Court (chief justice is appointed by the monarch after designation by the cabinet; all other justices are appointed by the cabinet) |
Political parties and leaders: | Democratic Party of Japan or DPJ [Ichiro OZAWA]; Japan Communist Party or JCP [Kazuo SHII]; Komeito [Takenori KANZAKI]; Liberal Democratic Party or LDP [Junichiro KOIZUMI]; Social Democratic Party or SDP [Mizuho FUKUSHIMA] |
International organization participation: | AfDB, APEC, APT, ARF, AsDB, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, CE (observer), CERN (observer), CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICFTU, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, LAIA, MIGA, NAM (guest), NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE (partner), Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), UN, UN Security Council (temporary), UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNMOVIC, UNRWA, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, WTO, ZC |
Flag description: | 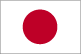 white with a large red disk (representing the sun without rays) in the centre |
Economy | Japan |
Economy - overview: | Government-industry cooperation, a strong work ethic, mastery of high technology, and a comparatively small defense allocation (1% of GDP) helped Japan advance with extraordinary rapidity to the rank of second most technologically powerful economy in the world after the US and the third-largest economy in the world after the US and China, measured on a purchasing power parity (PPP) basis. One notable characteristic of the economy is how manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors work together in closely-knit groups called keiretsu. A second basic feature has been the guarantee of lifetime employment for a substantial portion of the urban labor force. Both features are now eroding. Japan's industrial sector is heavily dependent on imported raw materials and fuels. The tiny agricultural sector is highly subsidized and protected, with crop yields among the highest in the world. Usually self sufficient in rice, Japan must import about 60% of its food on a caloric basis. Japan maintains one of the world's largest fishing fleets and accounts for nearly 15% of the global catch. For three decades, overall real economic growth had been spectacular - a 10% average in the 1960s, a 5% average in the 1970s, and a 4% average in the 1980s. Growth slowed markedly in the 1990s, averaging just 1.7%, largely because of the after effects of overinvestment during the late 1980s and contractionary domestic policies intended to wring speculative excesses from the stock and real estate markets and to force a restructuring of the economy. From 2000 to 2003, government efforts to revive economic growth met with little success and were further hampered by the slowing of the US, European, and Asian economies. In 2004 and 2005, growth improved and the lingering fears of deflation in prices and economic activity lessened. Japan's huge government debt, which totals 170% of GDP, and the aging of the population are two major long-run problems. Some fear that a rise in taxes could endanger the current economic recovery. Internal conflict over the proper way to reform the financial system will continue as Japan Post's banking, insurance, and delivery services undergo privatization between 2007 and 2017. |
GDP (purchasing power parity): | $3.914 trillion (2005 est.) |
GDP - real growth rate: | 2.4% (2005 est.) |
GDP - per capita: | $30,700 (2005 est.) |
GDP - composition by sector: | agriculture: 1.3% |
Labour force: | 66.4 million (2005 est.) |
Labour force - by occupation: | agriculture: 4.6% |
Unemployment rate: | 4.3% (2005 est.) |
Population below poverty line: | NA% |
Household income or consumption by percentage share: | lowest 10%: 4.8% |
Inflation rate (consumer prices): | -0.2% (2005 est.) |
Budget: | revenues: $1.429 trillion |
Public debt: | 170% of GDP (2005 est.) |
Agriculture - products: | rice, sugar beets, vegetables, fruit; pork, poultry, dairy products, eggs; fish |
Industries: | among world's largest and technologically advanced producers of motor vehicles, electronic equipment, machine tools, steel and nonferrous metals, ships, chemicals, textiles, processed foods |
Industrial production growth rate: | 1.3% (2005 est.) |
Electricity - production: | 1.017 trillion kWh (2003) |
Electricity - consumption: | 946.3 billion kWh (2003) |
Oil - production: | 120,700 bbl/day (2003 est.) |
Oil - consumption: | 5.578 million bbl/day (2003 est.) |
Oil - exports: | 93,360 bbl/day (2001) |
Oil - imports: | 5.449 million bbl/day (2001) |
Oil - proved reserves: | 29.29 million bbl (1 January 2002) |
Natural gas - production: | 2.814 billion cu m (2003 est.) |
Natural gas - consumption: | 86.51 billion cu m (2003 est.) |
Natural gas - exports: | 0 cu m (2001 est.) |
Natural gas - imports: | 77.73 billion cu m (2001 est.) |
Natural gas - proved reserves: | 39.64 billion cu m (1 January 2002) |
Current account balance: | $158.3 billion (2005 est.) |
Exports: | $550.5 billion f.o.b. (2005 est.) |
Exports - commodities: | transport equipment, motor vehicles, semiconductors, electrical machinery, chemicals |
Exports - partners: | US 22.7%, China 13.1%, South Korea 7.8%, Taiwan 7.4%, Hong Kong 6.3% (2004) |
Imports: | $451.1 billion f.o.b. (2005 est.) |
Imports - commodities: | machinery and equipment, fuels, foodstuffs, chemicals, textiles, raw materials (2001) |
Imports - partners: | China 20.7%, US 14%, South Korea 4.9%, Australia 4.3%, Indonesia 4.1%, Saudi Arabia 4.1%, UAE 4% (2004) |
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold: | $845 billion (2004) |
Debt - external: | $1.545 trillion (31 December 2004) |
Economic aid - donor: | ODA, $8.9 billion (2004) |
Currency (code): | yen (JPY) |
Exchange rates: | yen per US dollar - 110.22 (2005), 108.19 (2004), 115.93 (2003), 125.39 (2002), 121.53 (2001) |
Fiscal year: | 1 April - 31 March |
Communications | Japan |
Telephones - main lines in use: | 58.788 million (2004) |
Telephones - mobile cellular: | 91,473,900 (2004) |
Telephone system: | general assessment: excellent domestic and international service |
Radio broadcast stations: | AM 215 plus 370 repeaters, FM 89 plus 485 repeaters, shortwave 21 (2001) |
Television broadcast stations: | 211 plus 7,341 repeaters |
Internet country code: | .jp |
Internet hosts: | 21,304,292 (2005) |
Internet users: | 86.3 million (2005) |
Transportation | Japan |
Railways: | total: 23,577 km (16,519 km electrified) |
Roadways: | total: 1,177,278 km |
Waterways: | 1,770 km (seagoing vessels use inland seas) (2006) |
Pipelines: | gas 2,719 km; oil 170 km; oil/gas/water 60 km (2004) |
Ports and harbours: | Chiba, Kawasaki, Kiire, Kisarazu, Kobe, Mizushima, Nagoya, Osaka, Tokyo, Yohohama |
Merchant marine: | total: 683 ships (1000 GRT or over) 10,468,077 GRT/12,050,990 DWT |
Airports: | 173 (2005) |
Airports - with paved runways: | total: 142 |
Airports - with unpaved runways: | total: 31 |
Military | Japan |
Military branches: | Japanese Defense Agency (JDA): Ground Self-Defense Force (Rikujou Jietai, GSDF), Maritime Self-Defense Force (Kaijou Jietai, MSDF), Air Self-Defense Force (Koukuu Jietai, ASDF) (2006) |
Military service age and obligation: | 18 years of age for voluntary military service (2001) |
Military expenditures - dollar figure: | $44.31 billion (2005 est.) |
Military expenditures - percent of GDP: | 1% (2005 est.) |
Transnational Issues | Japan |
Disputes - international: | sovereignty dispute over the islands of Etorofu, Kunashiri, and Shikotan, and the Habomai group, known in Japan as the "Northern Territories" and in Russia as the "Southern Kuril Islands," occupied by the Soviet Union in 1945, now administered by Russia and claimed by Japan, remains the primary sticking point to signing a peace treaty formally ending World War II hostilities; Japan and South Korea claim Liancourt Rocks (Take-shima/Tok-do) occupied by South Korea since 1954; China and Taiwan dispute both Japan's claims to the uninhabited islands of the Senkaku-shoto (Diaoyu Tai) and Japan's unilaterally declared exclusive economic zone in the East China Sea, the site of intensive hydrocarbon prospecting |
Document Actions

 Like us on Facebook
Like us on Facebook