Veterinarian
Tasks & duties

Veterinarians working in clinical practice may do some or all of the following:
-
work with the client to prevent and treat animal problems and diseases
-
advise on animal nutrition and the care and welfare of animals
-
examine dead animals to find out the cause of death
-
work closely with herd and flock owners to help them achieve their breeding and production goals
Veterinarians working in other fields may do some or all of the following:

-
set standards for the importation of animals or animal products into New Zealand
-
negotiate with other countries to establish health requirements for animals or animal products exported from New Zealand
-
be involved with disease investigation and research and/or co-ordinate national disease control programmes
-
teach in tertiary institutes
-
research and advise on animal welfare
-
research and advise on animal breeding and production programmes
-
help pharmaceutical companies develop and market products used on animals
Specialisations
Veterinarians often specialise in treating either large or small animals. Some veterinarians may specialise further, for example in treating wildlife, poultry, horses, farm (production), zoo or companion animals.
Skills & knowledge
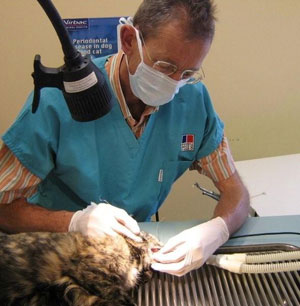
Veterinarians need to have:
-
knowledge of animals and animal diseases
-
animal-handling skills
-
knowledge of animal anatomy, physiology and biology
-
knowledge of biochemistry, microbiology and parasitology
-
skill in treating animals with medicines and performing surgery
-
knowledge of radiography, dentistry and laboratory methods
-
up-to-date knowledge of recent developments in veterinary science
-
communication skills
-
organisational skills
-
problem-solving and decision making skills
Business management knowledge may also be useful.
Entry requirements
To become a veterinarian, you need to complete a Bachelor of Veterinary Science.
Secondary education
A tertiary entrance qualification is required to enter veterinary training. Year 12 Certificate of Education or Higher School Certificate equivalent English, physics, chemistry and biology are preferred subjects.
Training on the job
Many skills are gained on the job. The Australasian Veterinary Boards Council Inc encourages veterinarians to continue their professional development by participating in ongoing learning activities in their area of interest.
Registration
Veterinarians need to be registered and they must obtain annual practising certificates.
Useful experience
Practical experience with farm animals such as work on a dairy, sheep or cattle farm, or work with domestic animals is an advantage. Other useful experience includes work as an animal technician in a research laboratory, animal training or any other work relating to the care of animals. Experience with other animal owners is also helpful.
Video
from WA career Centre on you tube
Related courses
Animal Husbandry
Veterinary Science
For more information, please refer to myfuture.
Document Actions
